Ransomware is a type of malicious software, or malware, designed to deny access to a computer system or data until payment of a ransom.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is malware that restricts access to a computer or network, and demands you pay a ransom to regain system control.
Generally, they request payment in digital currency due to the difficulty in tracking transactions.
Ransomware infects devices and encrypts files against payment via bitcoins or other cryptocurrencies.
Encryption can also occur during installation.
Victims can no longer open any file unless they pay a ransom.
Sometimes, attackers also delete backups and snapshots before encrypting them.
It is complicated for victims to restore their files without paying a ransom.
In recent years, ransomware attacks have become widespread and hit government entities, state or local, and critical infrastructure.
Especially hospitals and financial institutions.
According to Panda Security, 37% of all industries suffered a ransomware attack in 2021.

Is ransomware a virus?
Though most experts disagree, some features are similar to viruses.
Indeed, it can spread and infect new systems without the victim noticing it.
Ransomware takes over the computer by encrypting files until the victim pays to recover them.
After infecting a system, ransomware often spreads through USB drives or email attachments.
What is the biggest cybercrime?
Cybercrime has grown in recent years and is likely to increase further in the future.
This trend is strictly related to the need to ensure cybersecurity and growing digitization in daily life.
The FBI states ransomware is one of the most common crimes, among others:
- Email scams;
- Identity theft;
- Phishing;
- Online predators.
The U.S. federal agency emphasizes that users should take adequate security measures and be cautious when surfing the Internet.
Is ransomware a crime?
We may answer this question by simply referring to the Federal law of the United States, specifically to Computer Crimes and the Intellectual Property Section (CCIPS):
“This manual examines the federal laws that relate to computer crimes. Our focus is on those crimes that use or target computer networks, which we interchangeably refer to as ‘computer crime’, ‘cybercrime’, and ‘network crime’. Examples of computer crime include computer intrusions, denial of service attacks, viruses, and worms.”
OFAC and FinCEN warn that paying the ransom is against the law.
Who created the ransomware?
The biologist, Joseph Popp, was the creator of the first ransomware, as stated by CNN, among other networks.
In 1989, Popp mailed 20,000 floppy disks to the attendees of an AIDS conference.
After they entered them into their computer, the systems crashed, and a note appeared demanding a ransom of $189 to a post office box in Panama.

‘The incident created a lot of damage back in those days. People lost a lot of work. It was not a marginal thing — it was a big thing, even then’, said Eddy Willems, one of the victims.
The police arrested Popp and charged him with multiple counts, credited with being the inventor of ransomware.
Who is behind the ransomware?
Hackers typically propagate ransomware for financial gain or ideological reasons.
Some creators might be driven by financial motivations, such as making money by charging for decrypt files.
Some companies also use file encryption and engage in industrial spy ransomware to steal trade secrets or intellectual property.
Where do most ransomware attacks come from?
Most ransomware attacks originate in Russia and Ukraine, where most malicious websites offer cryptojacking malware to unsuspecting victims.
According to a study by blockchain company, Chainalysis, 74% of ransomware revenue in 2021 ($400 million) went to strains affiliated with Russia.

What does ransomware do?
Ransomware prevents users from accessing their data or programs until payment of a ransom.
Ransomware vectors are email attachments, malicious websites, and social networks.
Once it infects a computer, the ransomware encrypts all files on the affected device and demands payment to decrypt them.
The main goal of ransomware is to extort the victims to pay for the decryption key.
How does ransomware work?
Ransomware uses a variety of techniques to hit the target computer.
These methods include:
- Exploiting applications vulnerabilities;
- Infecting removable devices;
- Browser hijacking;
- Social engineering, such as phishing emails or fake websites.
The KnowBe4 report on cyberattack statistics shows that hackers stole login credentials in 85% of breaches linked to social engineering.

Once the ransomware has infected the target computer, it will encrypt the victim’s files and demand a ransom to decrypt them.
The ransom note shows up on a pop-up.
What can you do against ransomware?
If you have been a victim of ransomware, you will know that prevention is the best way to face it:
- Do not open suspicious emails or attachments;
- Use antivirus-protected software;
- Never download pirated software;
- Keep the operating system updated;
- Scan the computer after an update;
- Keep antivirus software up to date;
- Do not click on suspicious links or attachments;
- Beware of home networking equipment and wireless Internet;
- Keep the passwords of the printer and scanner in a separate document;
- Change passwords regularly on social media accounts and other websites;
- Do not leave shared files containing confidential information;
- Make backup copies of your files daily.
Contact HelpRansomware, which, among other services, offers ransomware prevention consulting.
The company has over 25 years of experience and specializes in ransomware removal, cybersecurity, and decryption.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
What is a ransomware attack?
Hackers attack to extort money from organizations, governments, or individuals.
Malicious software disable access to data or the entire system and demands payment of a ransom to restore normal operations.
Hackers threaten to delete the decryption key if they do not receive the ransom within a certain time frame.
How do ransomware attacks occur?
The ransomware attacks work by encrypting the victim’s files and then displaying a message demanding money to get the key for decryption.
These cyberattacks are more likely to occur through email attachments or links on social networking sites.
How long do ransomware attacks last?
The attack duration depends on how quickly the victim solves it.
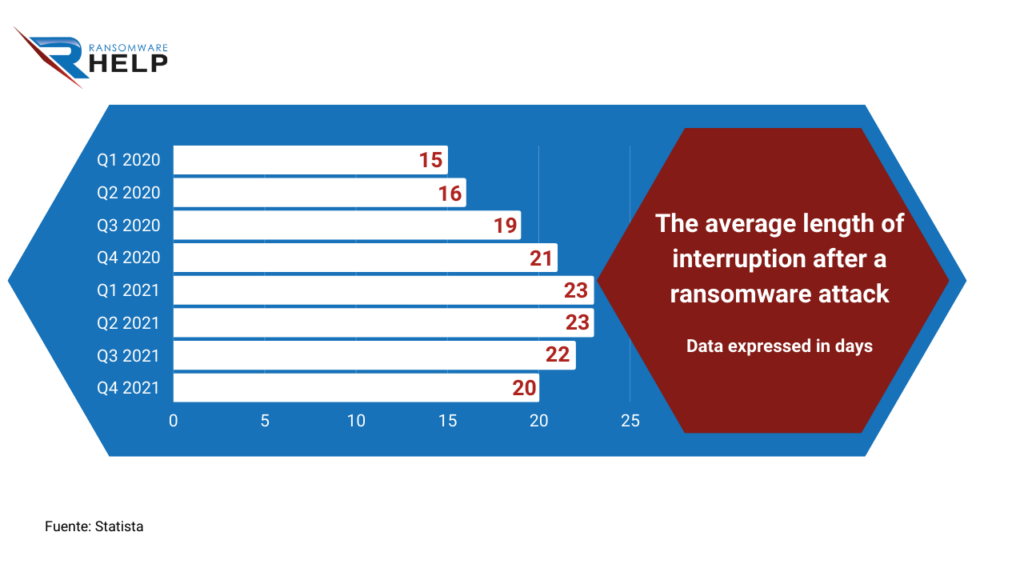
According to Statista, the average length of interruption after a ransomware attack on businesses was 20 days, in the fourth quarter of 2021.
The following infographic reveals how this figure had grown in comparison with the first quarter of 2020, showing 15 days.
Implementing appropriate security measures and following best practices helps mitigate ransomware attacks.
In addition, speed is essential, so you should rely on specialized companies such as HelpRansomware to improve it.
The company offers 24/7 global support and quickly removes the ransomware that encrypts files.
What is the worst ransomware attack?
The worst attack was WannaCry, which affected more than 230,000 computers in 150 countries.
This attack hit many organizations worldwide, including hospitals in the UK, FedEx in Spain, and Renault factories in France.
What are the impacts of an attack?
Ransomware can have devastating consequences for an individual or an organization.
According to the Sophos report, the average bill for rectifying a ransomware attack, considering downtime, people time, device cost, network cost, and ransom was $1.85 million.

Some victims pay to retrieve their files though there is no guarantee to restore them.
Recovery can be a tough process.
The best option is to rely on a specialist such as HelpRansomware.
Ransomware attacks can disrupt company operations and rob organizations of the data they need to function and deliver essential services.
Depending on the type of ransomware, the damage can be more or less superficial, but there are different solutions.
Ransomware attacks have become more destructive in terms of online reputation and costs.
What are the two main types of ransomware?
The two main types of ransomware are:
- Blocking ransomware: its function is to block a device’s basic activities by preventing access, for example, to the desktop.
The user can only interact with the warning window;
- Encryption ransomware: although it does not affect computer operations, it encrypts the most critical data and prevents the user from recover encrypted files.
HelpRansomware can help you in both cases, removing ransomware and decrypting data.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What is the most common ransomware?
Currently, the most common ransomware are:
- Stop Djvu;
- Makop;
- Checkmate;
- GlobeImposter 2.0;
- Clop;
- MedusaLocker;
- Sodinokibi;
- Babuk;
- LockBit 3.0.
Cybercriminals are constantly creating and testing new types of ransomware.
What is the most famous ransomware?
It depends. For example, a decade ago, it was CryptoLocker.
In 2017, the WannaCry attack reached up to 150 countries, and now LockBit.
What is the WannaCry ransomware attack?
The WannaCry ransomware attack was a cyberattack that occurred on May 12, 2017.
It is considered one of the largest in history and affected more than 230,000 computers in more than 150 countries.
The fraudsters performed the attack using the EternalBlue exploit leaked by Shadow Brokers Group. The malware encrypts the files on a computer and then displays a message demanding payment in bitcoins to decrypt them.
This attack mainly pointed to computers running Microsoft Windows devices, although other platforms were also affected.
What is DarkSide Ransomware?
DarkSide ransomware encrypts data on an infected computer and then demands a ransom to decrypt it.
It is one of the most common types of ransomware today and one of the most dangerous.
This ransomware typically hacks users’ computers via an email attachment or a portion of a file downloaded from the Internet.
It will search the system for files and encrypt them using powerful encryption algorithms, once installed.
You will then display a note demanding payment to decrypt the files and return them to their original state.
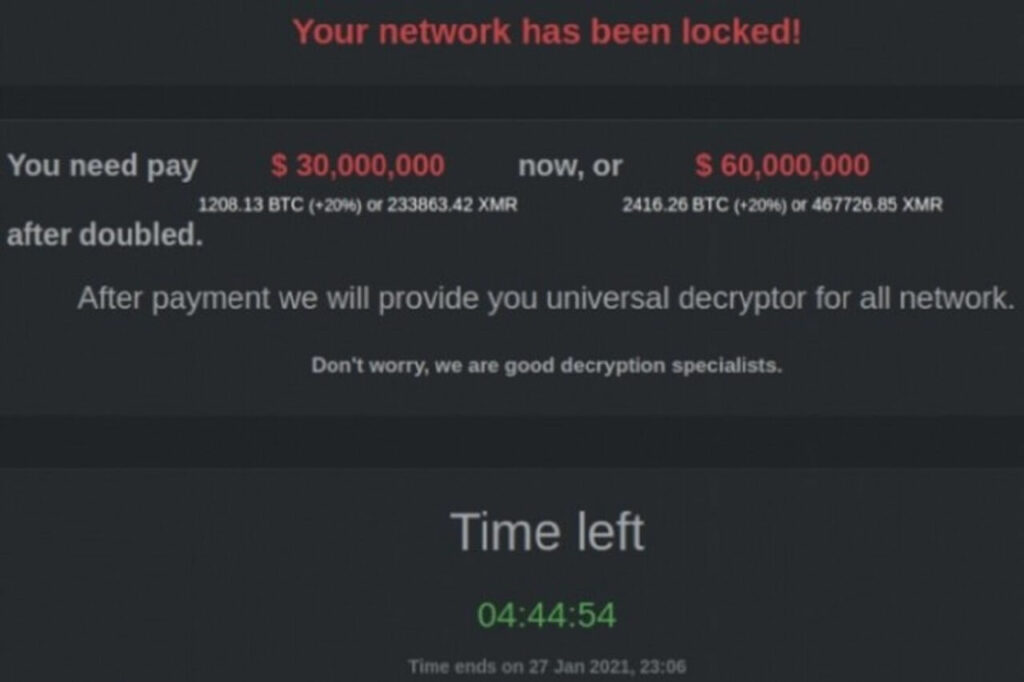
Even if you are a victim of DarkSide, you should never pay the ransom demand because there is no guarantee that they will decrypt the files after the payment.
Do hackers use ransomware?
Hackers use ransomware to break into a computer system and demand payment to release user data.
It usually runs through a Trojan that the user downloads and opens.
Ransomware encrypts a user’s files and deletes them if the victim does not pay.
It often includes instructions on how to proceed with payment.
How do cybercriminals use ransomware to attack their victims?
Malicious cyber attackers are continuously adapting their ransomware tactics to extort victims.
They may threaten to publish their data if they refuse to pay the ransom.
Or better, double extortion, to avoid publishing that information.
Alternatively, attackers target critical data and spread ransomware over entire networks.
They adopt different tactics, like system backups removal, which makes it difficult to restore files.
How do hackers install ransomware?
Hackers often install ransomware by sending an email with a link to the victim or luring them to malware-infected sites.
Many users do not know they are being infected and may not notice any changes in their system until they pay the ransom.
A pop-up window usually appears with a red padlock and an exclamation mark.
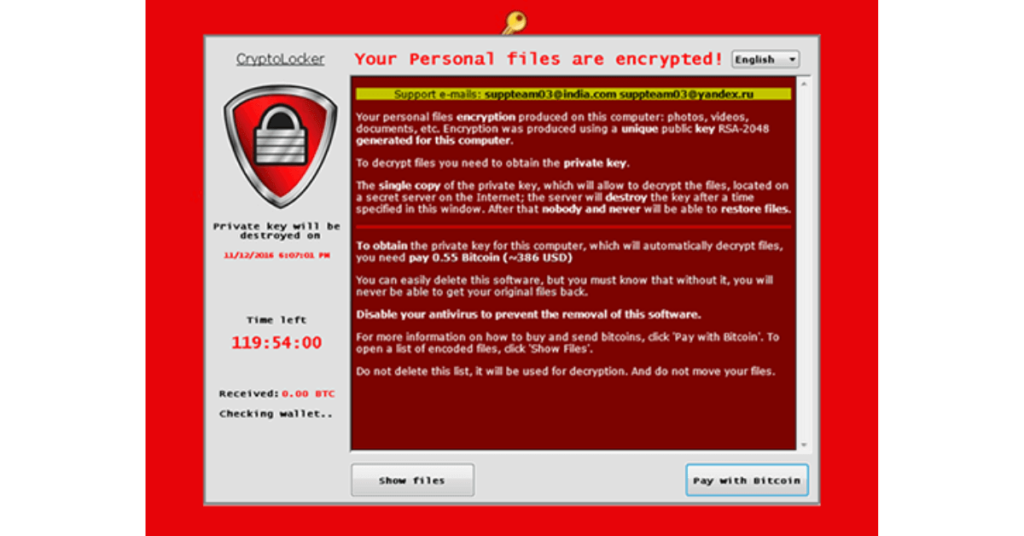
It means your files are encrypted, as this type of code usually has a decryption key for each user.
To decrypt the files, you will need the same decryption key.
Ransomware victims fear they will never retrieve their data if they do not pay, so they have no choice but to come across.
However, this is not the case: payment does not guarantee data recovery and only encourages cybercrime.
The most efficient and immediate option is to contact a ransomware company like HelpRansomware.

Expert Ransomware Removal
Our certified professionals have over 25 years of experience in ransomware removal, data recovery, and computer security.
How does ransomware spread?
Ransomware propagates through the following vectors:
- Email: ransomware can reach your email box through an attachment.
Once opened, the user data are encrypted, and you receive a warning to pay a ransom for data recovery;
- Drive-by downloads: this method uses ransomware through infected websites or by visiting a website with infected ads or software. Ransomware download on the computer prevents victim interactions.
These are the two main ways of spreading ransomware, which takes advantage of system vulnerabilities.
How fast does ransomware spread?
Ransomware can spread very quickly if you do not detect it in time.
It usually takes less than an hour to propagate.
Instead, more advanced ransomware like WannaCry took several days to spread globally.

It infected 10,000 computers every hour, according to Avast data.
Can ransomware spread over Wi-Fi?
A study by the University of Liverpool showed that the virus infects Wi-Fi networks.
They verified it was able to avoid detection and identify the points where access is least protected by encryption and passwords.
Alan Marshall, Professor of Network Security at the University, said: ‘Wi-Fi connections are increasingly a target for computer hackers because of well-documented security vulnerabilities, which make it difficult to detect and defend against a virus.’
Can ransomware infect mobile phones?
Ransomware can reach any device connected to the internet, including smartphones.
Recently, ransomware attacks on mobile devices have fallen.

According to a Kaspersky study, the number of attacks on mobile users worldwide reached 46 million in 2021.
This figure decreased by 36% compared to 63 million in 2020.
Can ransomware infect USB?
Yes, it can. The ransomware may infect a USB even if it is not encrypted.
Malware can spread over the computer network and encrypt files on other computers and reachable devices, such as a USB drive that was left plugged in.
How long does it take for ransomware to encrypt files?
Ransomware encrypts files using a public key and a private key.
The malware generates the public key when it starts and then encrypts the files. The private key is not available until the victim pays the ransom.
This ransomware process usually takes almost one hour to encrypt all files on a computer system.
But it can also take days, weeks, or even months.
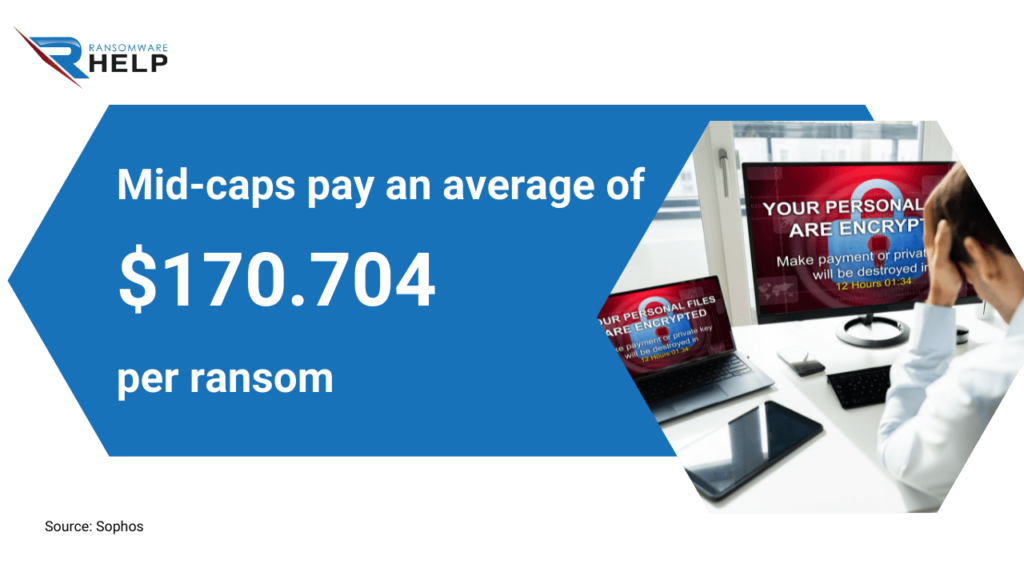
The cost of data recovery depends on the type of ransomware and the number of encrypted files.
The Sophos report indicates that mid-caps pay an average of $170,704 per ransom.
Does ransomware steal data?
Unlike traditional data theft, ransomware is specific for file encryption.
Its main objective is to block the victim’s information and extort money.
In 2021, 59% of attacks used a double extortion strategy, as explained in the IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index report.

For its part, malware infects a computer without being detected and performs any number of tasks, such as stealing data.
Can ransomware get my passwords?
The answer is yes, but it depends on which malware infects your PC.
The ransomware malware encrypts files and requires payment of the decryption key to unlock them.
There are two types of ransomware: the first encrypts the files and requires payment of the decryption key, while the second deletes your data if you do not pay.
Ransomware can spread through other malware without notice, so you must be vigilant when downloading software or opening attachments that may compromise the system.
Can ransomware be removed?
You can remove ransomware using anti-ransomware tools such as Norton, Malwarebytes, or Kaspersky.
In addition, some antivirus software can help remove ransomware from your system, for free.
Decrypting files is complicated, so you should better turn to a specialized company to carry out this process.
HelpRansomware can help you in both deleting and recovering data.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
Does resetting computer remove ransomware?
Resetting your computer will remove any malware installed previously, but it will not undo ransomware changes, such as file encryption.
It is always better to back up your data before restarting your computer and make sure you have good antivirus software installed on your computer.
Will reinstalling Windows remove ransomware?
Two factors should be taken into account when answering this question.
The first is how the ransomware got to the computer, and the second depends on the operating system.
If you are using Windows 10, it would be safer to reinstall Windows without worrying about removing the ransomware.
However, if you have an older version of Windows, the infected files may not appear after you reinstall Windows.
Does shutting down your computer stop the virus?
The most common way to stop ransomware is to avoid shutting down the computer.
Instead, you should stop the process that is running on your computer.
However, it will not work if too many processes are running or if one of your files hides the process.
In this case, you should turn off your computer.
How much does it cost to remove ransomware?
It is difficult to estimate the cost of remove ransomware.
You should ponder more factors, such as the type of ransomware, the volume of encrypted data, and the resources available.
Some types of ransomware require a professional removal service, while others are easy to delete.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
In the case of HelpRansomware, its professionals establish four steps for a safe, fast, and efficient removal:
- Urgent assessment: the victim submits the case, sending the encrypted data for a first urgent assessment;
- In-depth analysis: a thorough analysis of all encrypted data will help determine the cost for recovery;
- Quick Quote: in one day, the team sends the quote with accurate information about costs and processing times;
- Guaranteed deletion: once you accept the quote, the HelpRansomware team starts the ransomware removal and data recovery.
Contact a specialist at HelpRansomware, the world’s number-one ransomware removal company.
Which antivirus can remove ransomware?
The best way to protect your computer against ransomware is to have an antivirus installed on your system.
If you are using a Windows computer, we recommend installing Windows Defender, integrated into the operating system for free.
Many third-party antivirus tools offer additional features such as anti-malware and web browsing protection.
For example, McAfee and Kaspersky Lab products, but there are many other options.
Should I report ransomware to the police?
Most of the time, authorities cannot help recover files.
They generally focus on peeking at cyber criminals and preventing future attacks but cannot help victims of ransomware attacks.
If you decide to report a ransomware attack, make sure you have all the necessary information, such as your IP, email address, and other relevant details.
What happens if you pay for ransomware?
By paying the ransom, you should get a ransomware decryption key or other unlocking software to unplug your device.
However, there are also chances that cybercriminals will not unlock it even after they receive payment.
The Sophos survey indicates that only 8% of organizations got data back.

Paying demonstrates your vulnerability and hackers will persist in demanding more money.
How to pay for ransomware?
There are three ways to pay the ransom:
- Bitcoin: is an anonymous digital currency that consumers use to purchase products.
It does not require any personal or identifying information to use, which makes it easier for criminals to use it for their transactions;
- Moneygram: is one of the most popular money transfer services in the world, with offices in more than 200 countries and territories worldwide;
- Western Union: operates since 1851 and has offered money transfer services for more than 140 years.
Today, cryptocurrency is the most common form of ransom demand by hackers.
According to a document released by the United States Senate Committee on National Security and Government Affairs, cyber criminals received $692 million in cryptocurrencies as a result of ransomware attacks.

Do companies pay for ransomware?
There are two ways in which companies can retrieve their data from a ransomware attack.
One is paying the ransom. It may seem the easiest way to recover data, but it is not always the best choice for companies.
Paying the ransom does not guarantee that they will get their data back.
It also encourages more ransomware attacks because hackers know they can make more money.
The second option is to contact a company specializing in data recovery.
HelpRansomware can help you remove the ransomware and open encrypted files.
Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
By doing so, cybercrime is not encouraged, and you will surely recover the encrypted files.
Should I pay a ransom to hackers?
The answer is simple: you should never pay a ransom for encrypted data.
Even if it seems the right way, it is not because hackers will ask you for money again by taking advantage of your vulnerability.
Can you protect yourself from ransomware?
Protecting yourself is easy by applying the following tips:
- Backups: have a backup of your files on an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
Making a regular copy of an older version of your files available may also help if something goes wrong.
This way, if ransomware infects your computer, you can replace the files with a backup;
- Software: you must also purchase anti-malware software and make sure it is up to date;
- USB: If you have a USB drive, use it to back up your computer.
Ransomware protection is the best prevention against infection with this type of malware.
What is the best protection against ransomware?
The most important thing you can do to protect yourself is to have a backup to restore your files encrypted by ransomware.
You should also keep your computers up to date with the latest software versions and avoid downloading pirated software.
Does a VPN protect you from ransomware?
It is not true that a VPN protects against a ransomware attack.
Your computer is more vulnerable when connecting to a different IP.
Indeed, ransomware often links to applications or pop-ups that appear while the user is browsing the Internet.
Are there precautions against ransomware?

The following precautions can protect you from the threat of ransomware:
- Update your software and operating systems with the latest patches.
Obsolete applications and operating systems are the targets of most attacks;
- Do not click on links or attachments inserted in unsolicited emails or whose sender you do not know;
- Back up your data regularly and store it on a separate device or offline.
This operation does not prevent an attack, but it will surely help minimize data loss;
- Browse safely when devices connect to the Internet.
You should apply these tips for better protection against ransomware.
What are other best practices against ransomware?
These small steps are helpful for ///individual/// ransomware victims but also for organizations:
- Restrict user permissions to install and run software applications and apply the ‘minimum privilege’ principle to all systems and services.
Limiting these privileges may prevent malware from running or at least restrict its ability to spread over the network;
- Use the application authorization list to allow only approved programs to run on a network;
- Enable powerful spam filters to prevent phishing emails from reaching end users and authenticate incoming emails to prevent email spoofing;
- Scan all incoming and outgoing emails for threats and filter executable files so that they do not reach end-users;
- Configure firewalls to block access to known malicious IPs.
If you are a ransomware victim, do not waste your time and turn to HelpRansomware to minimize the damage.
Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
Who is at risk of a ransomware attack?
Computers with an Internet connection and sensitive data stored on a computer or network are at risk.
Government agencies, authorities, and health care systems are not immune; in fact, they are frequently the preferred victims because of the nature of the information they keep.
What percentage of ransomware victims pay the ransom?

The Thycotic 2021 report shows that 83% of attack victims had no choice but to pay the ransom demands.
How does ransomware affect my business?
Ransomware attacks can be devastating for businesses.
Ransomware does not only affect companies’ data, crippling the work rhythm, but it also damages the brand and corporate reputation.
The attack also has economic consequences for businesses.
According to the 2022 Global Cybersecurity Outlook report, 14 market days after a breach becomes public, the average share price underperforms the NASDAQ by -3.5%.

The best way to protect your business from ransomware is through prevention.
That means using strong passwords, installing software updates on all devices, and antivirus to protect your computers.
You should also back up your data regularly.
Which companies have been hit by ransomware?
Although companies do not want to be associated with ransomware attacks to protect their digital reputation, this malware targets many.
Some recently affected companies are NBA, Accenture, Geox, Fujifilm, and Acer.
Examples of Ransomware
At the end of August, TAP Air Portugal was the victim of a ransomware attack.
The company communicated the fact and asked customers to protect their accounts, since their data had been leaked on the Dark Web.
Another example is the ransomware attack that hit Whitworth University.
It took over a month for the private university in Washington to restore 95% of operations.

What is an example of a ransomware attack?
Although this guide names and illustrates ransomware examples for companies, the same is true for institutions.
One of the most notorious attacks hit the Government of Costa Rica.
The country president announced it, naming this type of ransomware: Conti.
He then declared a state of emergency in the country for cybersecurity reasons.
How long does it take to recover from ransomware?
Companies take two to four weeks to return to normality.
Therefore, it is crucial to trust a company that works urgently to return to routine as soon as possible.
How are ransomware attacks resolved?
On the one hand, if your system is free of infection, you can remove it with software.
If you do not detect it before infection, you can restore encrypted files without paying the ransom.
Can a company recover from ransomware?
Recovery from ransomware is possible. However, the process is difficult and time-consuming.
Understanding the type of ransomware and its effects on the company is the first step toward recovery.
Then, determine what data was lost and how it was encrypted.
It will help detect corrupted and unaffected files.
You can save time by contacting a specialized company like HelpRansomware, an expert in ransomware removal, cybersecurity, and decryption.
DO YOU NEED HELP NOW? ENG
Conclusions
Through this HelpRansomware guide, you have discovered all the information and resources about ransomware.
We can draw the following conclusions from this article:
- Ransomware restricts access to files on a computer until payment of a ransom;
- Bitcoin is the main currency demanded in the ransom requested by cyber criminals;
- It spreads like a virus infecting systems without the victim’s knowledge//being aware of it//notice;
- Ransomware is a crime, as well as paying ransom for data recovery;
- Joseph Popp was the creator of the first ransomware;
- Most of the ransomware attacks come from Russia and Ukraine;
- WannaCry is considered the worst/most powerful ransomware attack in history, carried out in 2017;
- The average expense for neutralizing ransomware is $1.87 million;
- Mobile phones are also the target of ransomware;
- It is vital to have backup copies and updated software;
- The consequences of the attack are devastating for a company’s revenue and damage its reputation.
Ransomware attacks have increased In recent years, affecting companies and government entities.
Although you can remove ransomware with software, data encryption adds complexity.
To restore the files you have on your computer, you need to contact an external company specialized in decryption.
But never pay the ransom demanded by cybercriminals.
HelpRansomware can help you remove the ransomware and open encrypted files.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.




