By reading the new HelpRansomware guide on phishing, you will discover: what it is, how it works, the types, what are its consequences, and how to avoid it [GUIDE 2022].

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
What is phishing?
Phishing is one of the cheapest, easiest, and most effective ways cybercriminals access confidential information. It is also known, in many cases, as CryptoLocker.
By simply clicking a link, victims can put their company’s security at risk by leaving important confidential information unattended.
Just as it attacks an organization, the virus can also attack your personal data: usernames and passwords, as well as financial information, such as credit cards, etc.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines phishing as :
“An attempt to trick someone into giving information over the internet or by email that would allow someone else to take money from them, for example, by taking money out of their bank account.”
How does phishing work?
It starts with a scam email or other communication designed to entice anyone to check their inbox.
Most phishing campaigns use one of these methods:
- Attachments: email attachments, usually with catchy names that, when opened, install malware on your computer;
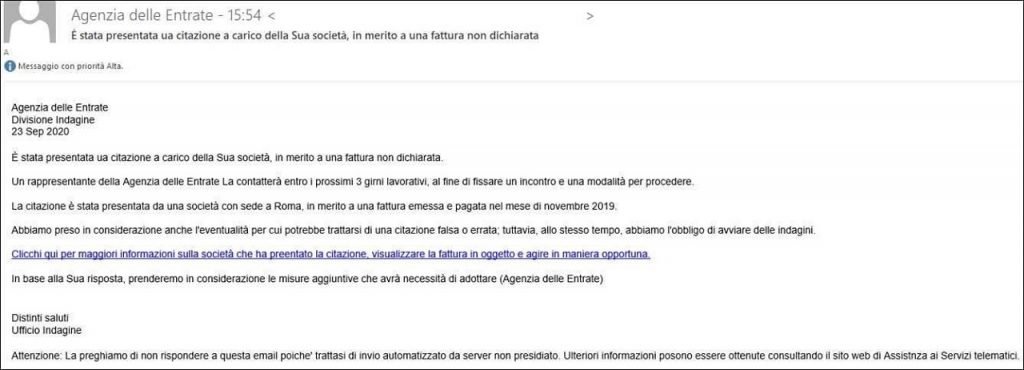
- Website links: hackers often use them to lead to legitimate clones, malware downloads, or login pages containing credential collection scripts.
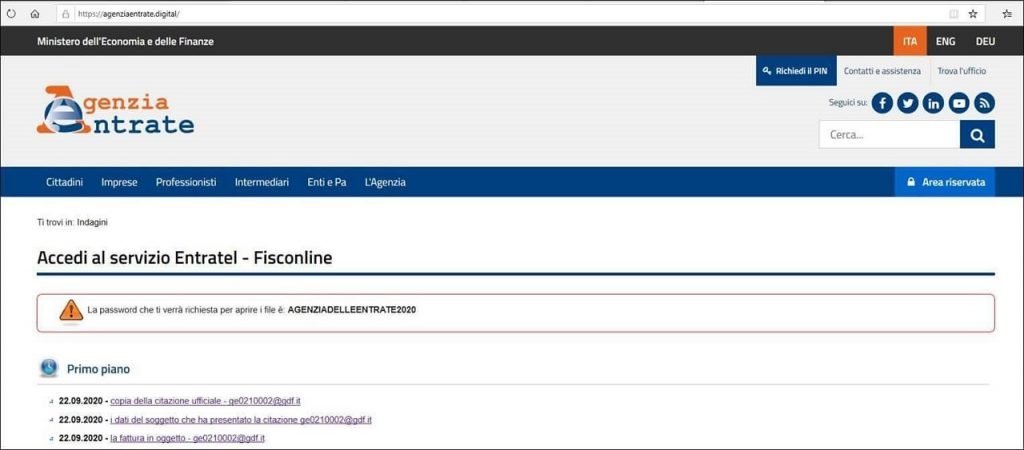
What kind of attack is phishing?
As we said earlier, phishing is a type of social engineering attack, which according to Enisa:
“Refers to all techniques aimed at talking a target into revealing specific information or performing a specific action for illegitimate reasons”.
Therefore, scammers require personal data from you, such as your credit card information, to obtain financial gain.
In this way, they can obtain all the information of customers and workers at the company level and access locked or inaccessible files, company funds, even damaging their reputation.
Those who engage in this type of cybercrime must have high IT skills and previous experience in the sector.
How does the phishing virus spreads?
The primary means to spread the virus is email.
By pretending an identity is known to the user, the hacker throws his bait.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
The most common ways to spread viruses are:
- By downloading a file:
When you download a file without knowing that it contains the phishing virus – a Trojan horse or something similar, apparently harmless, will be executed on your device – it will help install a script capture program instead.
This grabber will save everything you type on the keyboard, including usernames and passwords.
There are free ransomware decryption tools that can help you decrypt your data.
- By opening a link:
You are redirected to a fake web page that requires you to enter your details by clicking on a link. This page looks almost identical to the original website.
Once you try to log into your account, in this case, they will ask for more information than the actual page would:
- Name and address;
- Account number and password;
- Your card number and your security code.
Sometimes the malware includes ransomware that makes its way through the victim’s network, by encrypting and exporting sensitive data to demand a ransom.
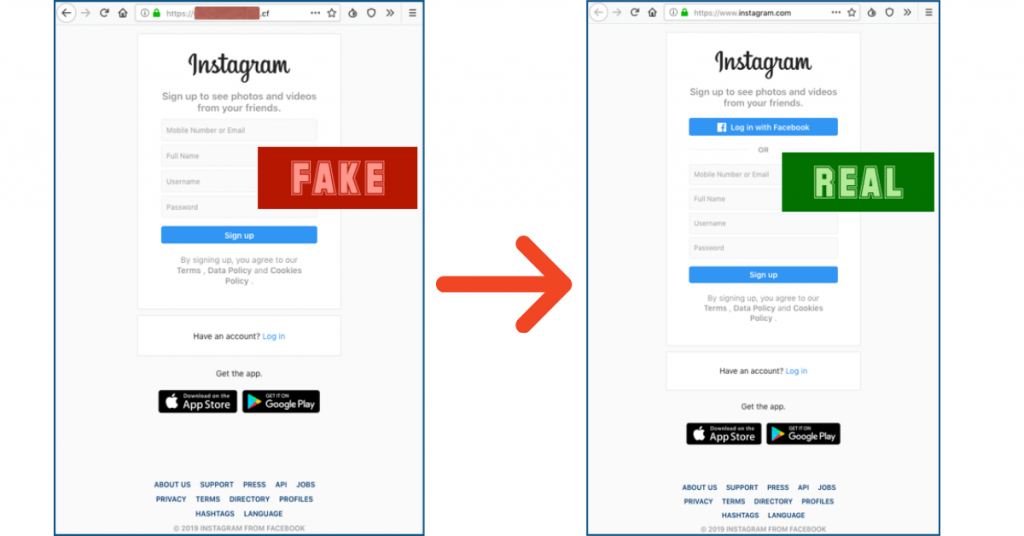
Minor typos or inconsistencies with the domain often reveal its true nature.
These domains are known as Typosquatting domains. According to WordSense Dictionary typosquatting is:
“A form of cybersquatting that involves the registration of domain names likely to be mistyped by users, e.g. exmaple.com for example.com.”
Phishing is a type of sneaky cyber attack, which everyone should be aware of to protect themselves and secure the company’s email.
If you have been a victim of phishing cases, do not hesitate to contact experts like HelpRansomware.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
Types of phishing
Phishing comes in many forms.
A hacker whose goal is to steal companies’ financial information uses different techniques than someone who attempts to access confidential data.
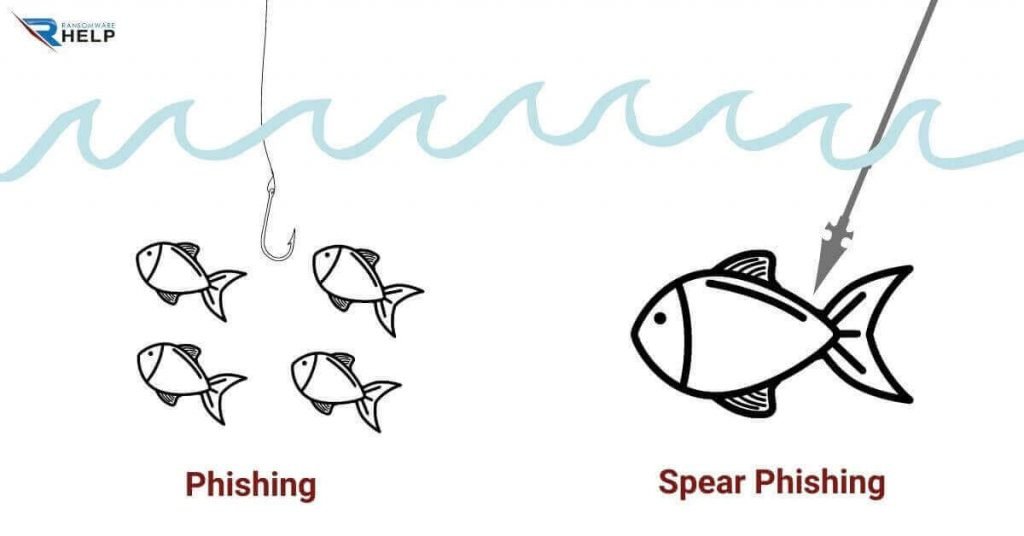
The most common examples of phishing include deceptive phishing and spear phishing, most of which occur via email.
Spear phishing
Spear phishing is similar to traditional phishing, the difference being that instead of applying on a large scale, it is aimed at a limited and specific group of people, such as the CEOs of a company, for example.
These types of attacks work through email.
The crackerjack sends a message on behalf of a credible organization, company, or sender with whom the victim is already in contact.
For this reason the content of the message is the bait and, just one click is enough to fall into the trap.
The deceiver leads the victim to a website, where he asks to enter confidential data. The data breach happens once the thief has the information.
Whaling
Whaling refers to that non-traditional type of fishing, for which you try to get the biggest fish to bite.
The prototype of the malicious one is an ambitious scammer who targets those at the top of companies.
These hackers thoroughly study the users they want to deceive.
They, too, use email as the primary tool to achieve their goal.
Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
Whale hunters pose as chief executive officers, senior and finance directors, HR chiefs, etc.
Thus, they try to persuade the victim to reveal valuable confidential information.
They use jargon that reflects their profession to induce them to open the malicious link and, as a result, access the confidential information that is supposed to be handled by these personalities.
Pharming
Pharming and phishing are very similar, but not the same.
As the name suggests, phishing uses bait: hackers send real-looking emails, invite victims to visit fake sites, and trick them into entering personal information.
On the other hand, Pharming skips this step and misdirects victims o fake websites without their knowledge.
It consists of a DNS cache tampering attack, which Google support defines as:
“The DNS (Domain Name System) is a hierarchical naming system for computers and other resources connected to the Internet. It is a kind of Internet address book since one of its primary functions is to associate domain names with IP addresses.”
The purpose of this attack is to convert a website‘s alphabetical name into a connected IP address.
In simple words, the hacker can redirect users to a malicious website of his choice.
It is one of the most advanced methods of identity theft.
Smishing and vishing
Cybercriminals use mobile phones as an effective scam device since they know that most people can’t live without them at all.
Smishing (SMS phishing) is a cybersecurity attack carried out over text messages.
Like emails, text messages have misleading content, encourage people to download documents or links that contain malware.
Vishing (voice phishing) scams are conducted over the phone where the cybercriminal tries to persuade people to share specific personal data by posing as a company staff employee.
These scammers can easily disguise the caller ID, so the call appears to be from a local area or a legitimate company phone number.
Meanwhile, Google has released a configuration method to avoid phishing emails and ensures that:
“You can protect incoming mail against phishing and harmful software (malware). You can also choose what action to take based on the type of threat detected.”
How does phishing on Facebook works?
Facebook phishing is a way to create a fake by imitating the web pages of this famous social networking site.
Scammers steal account credentials and PII, financial information such as credit cards, performing identity theft.
Why Facebook?
We know that cybercriminals’ goal is to reach as many victims as possible in the easiest way. Social networks are perfect since they satisfy both characteristics.
Facebook is the social networking giant, it has the most significant number of users, and the numbers are likely to increase in the coming four years.
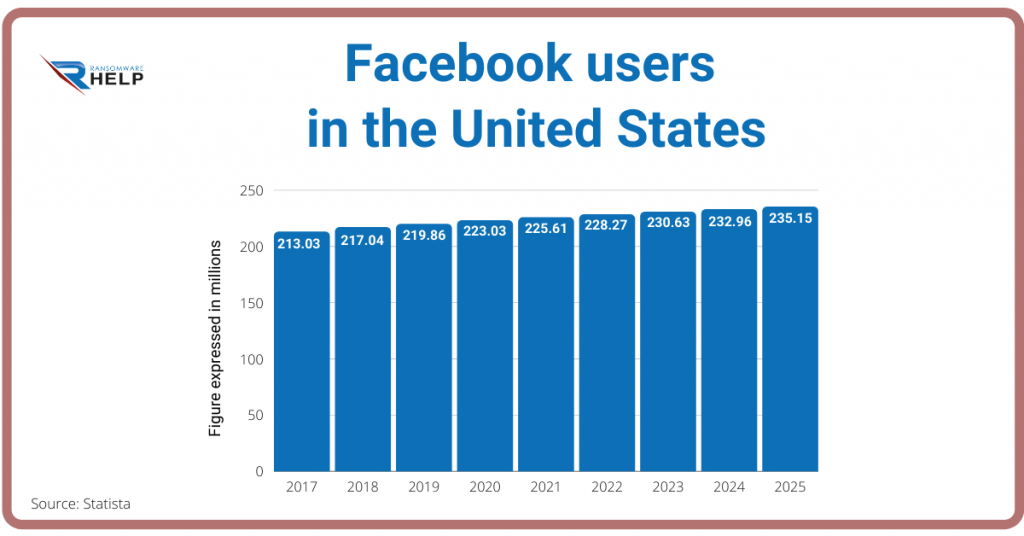
In 2021, the number of Facebook users in the United States should be over 225 million and reach 235.15 million by 2025. As of the first quarter of 2020, 2.6 million users accessed the social network.
This social platform hosts billions of usernames, passwords, personal data, and financial information, all willingly supplied by users.
The most common phishing attack is performed by sending phishing emails and links from a fake Facebook login page to obtain the victim’s account details.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What do phishing emails look like?
Email phishing is commonly achieved by using domains of legitimate companies and persuading users to download a malicious link.
When you suspect that fraudsters impersonate a well-known company, look at the domain name, usually misspelled or with additional subdomains.
You may spot phishing emails when they:
- say they have noticed some suspicious activity or login attempts;
- claim there is a problem with your account or your payment information;
- say you must confirm some personal data;
- include a fake invoice;
- want you to click on a link to make a payment;
- say you are eligible to register for a government refund;
- offer a coupon to get free products.
How to recognize a phishing message?
Detecting a phishing message might seem easy, but it is not, and this is why scam attempts have been increasing over the years and spiked during the pandemic.
Thanks to these suggestions, however, you will learn to spot them quickly.
We know that cybercriminals go to great lengths in designing phishing messages to mimic actual emails from a spoofed organization.
They use the same formulas, formatting, logos, and signatures that look like those as in the original message.
In any case, the sender name appears dubious, so you should be careful about who is sending the email.
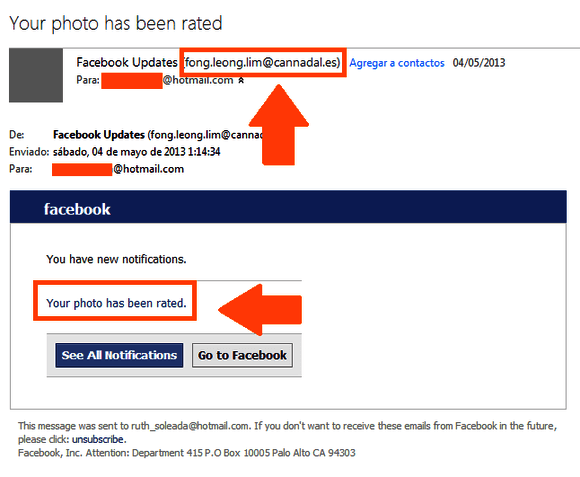
For example, you can see from the picture above that the sender’s name has nothing to do with Facebook.
Conversely, assuming you click on the link, you will be directed to a malicious webpage with a URL that contains additional names:
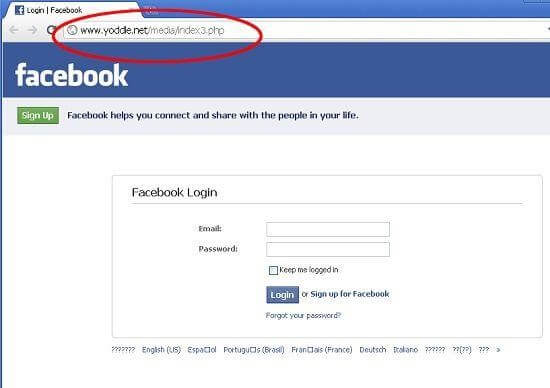
The URL, once again, has nothing to do with the official Facebook page.
How to avoid phishing
Activating the so-called “spam” filter is not enough to prevent email phishing. Hackers will always find ways to bypass all types of filters.
For this reason, you need to strengthen your digital and financial network security.
HelpRansomware, offers you four tips to protect yourself from phishing by:
- securing your computer and mobile devices with security software and automatic update;
- double-checking the email senders’ name;
- paying attention to the domain name;
- making a data backup copy through an external hard drive independent from your wireless network connection.
Examples of phishing
As we explained earlier, there are several types of phishing, but the most common are:
- email phishing, a scam technique often used to steal user data;
- fake attachments designed to trick you into installing malware on your computer;
- malicious links which redirect you to a website that encourages you to enter your personal information.
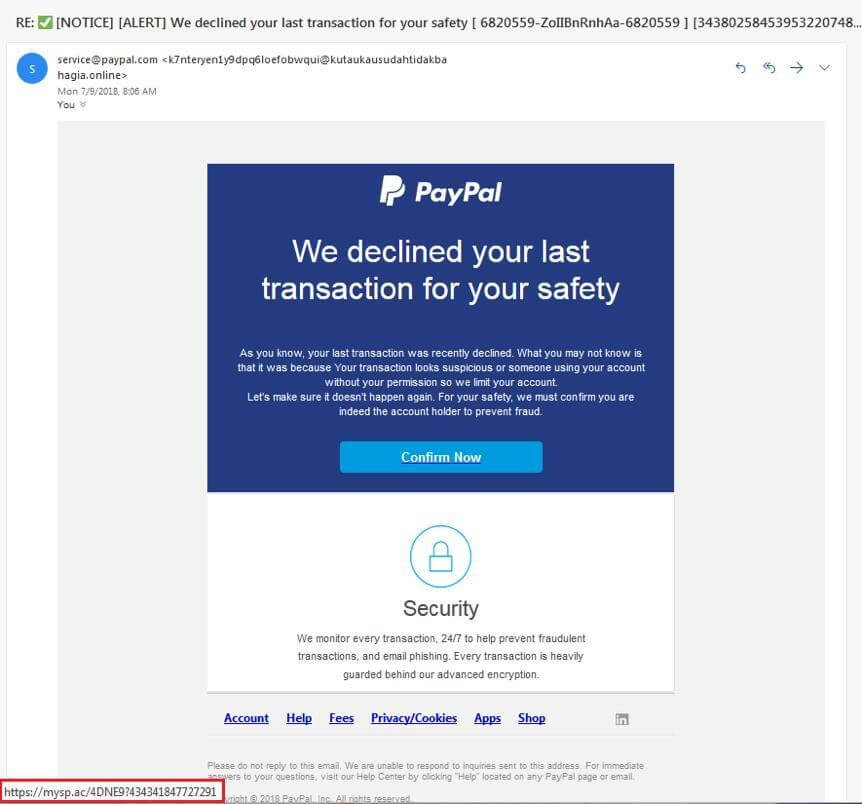
These are some examples of phishing emails that well-known companies receive:
- they get an email not addressed to them;
- it contains grammatical errors;
- scammers attempt to lure the victims with messages like “your account has expired” or “your payment has been declined”;
- by hovering the mouse over the link, you can see the URL and know whether or not the message is legitimate.
What are the consequences of phishing?
The consequences of phishing may result in:
- losing access to your email;
- identity theft and banking fraud;
- downloading viruses and malware;
- ransomware attacks that typically demand a ransom payment;
- data breach of credit card, account numbers, and verification codes;
- download attack and security breach through access to corporate data and networks.
How to protect yourself from phishing?
As we have already explained, phishing is mainly related to email.
Here are some tips to help protect yourself against this cybercrime.
If you have already been a victim of phishing, do not hesitate to contact HelpRansomware. We will provide professional and practical assistance to protect your organization against cyber attacks.
Meanwhile, we have listed a few easy steps for timely action:
- log in to your user account and change your password to kick the hacker out;
- get in touch with the impersonated organization and report what happened;
- scan your computer for viruses and malware;
- monitor bank statements;
- contact HelpRansomware to get an effective quality service.
Conclusions
This HelpRansomware guide thoroughly explains what phishing is and how cybercriminals access confidential information.
We can, therefore, conclude that:
- phishing begins with a fraudulent email or other communication enticing users to check their inbox;
- emails might include a file to download malware or a link to a malicious page;
- there are different types of phishing: spear phishing, whaling, pharming, smishing, and vishing;
- Facebook phishing is one of the most effective scams as it uses the most prominent social media networking worldwide;
- phishing emails look genuine and legitimate; now you know how to spot the differences;
If you have experienced a cyberattack, do not hesitate to contact HelpRansomware specialized in ransomware decryption and data recovery.
With state-of-the-art technology, sophisticated business techniques, and a team of cybersecurity experts, we provide recovery, removal, and prevention services.
We will treat your case as a high priority so that you can start working as soon as possible.

Expert Ransomware Removal
Our certified professionals have over 25 years of experience in ransomware removal, data recovery, and computer security.




