Read on to find out what double extortion ransomware is, how to avoid It, and its risks. You will see how it works and discover the main families.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
What is double extortion?
Double extortion is a form of extortion in which the victim is forced to pay the perpetrator twice.
Therefore, double extortion ransomware works by twice asking the victim to pay the ransom.
The first time the malware penetrates your device, it encrypts all the files and data it finds and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Subsequently, hackers threaten the victim to publish the stolen information on the Internet.
To prevent this, they ask to pay once more.
According to the survey conducted by Sophos, the average ransom paid increased nearly fivefold to $812,360 compared to the previous year.

Another term to define double extortion ransomware is ‘double-dipping’ ransomware.
Double extortion meaning
The notice promulgated at the end of 2021 by FinCEN, the US organization against financial crimes, states that cybercrimes with double extortion are growing.
It explains how these attacks occur:
‘They involve removing sensitive data from targeted networks, encrypting system files, and requesting a ransom. Cybercriminals, therefore, threaten to publish or sell stolen data if the victim does not pay. Other patterns of extortion have also emerged whereby cybercriminals use the system breach to target third parties related to the initial victim, such as their business partners or customers, and attempt to identify subsequent targets.’
In both cases, cybercriminals make double extortion with a double demand for blackmail.
Origins of double extortion ransomware
The origins of double extortion ransomware are traced back to the first ransomware attack.
HelpRansomware experts constantly urge not to pay the ransom because once attackers receive the money, there is no guarantee of recovering the data.
Cybercriminals can return to the victim at any time and issue new threats.
Indeed, this type of extortion has risen dramatically in recent years.
It is due to various factors, primarily teleworking and the digitization of many infrastructures, such as healthcare.

According to estimates by CipherTrace, double extortion ransomware increased by nearly +500% in 2021.
When did the double extortion start?
The double extortion ransomware technique has been around since 2013; it came back strongly on the scene in 2019.
That year, a criminal organization called TA2101 used Maze ransomware to carry out a double extortion attack.
The BleepingComputer agency discovered the data breach through an email signed ‘Maze Crew.’
The victim was Allied Universal, a prominent American provider of security systems and services.
Instead of proceeding with standard encryption via ransomware, the TA2101 group exported the data and threatened the company to publish them online.
The condition for not exposing the data was to pay a ransom of $2.3 million in bitcoin.
How does double extortion ransomware work?
A double extortion ransomware attack is similar to the so-called Advanced Persistent Threat (APT).
As reported by the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Security):
‘They allow it through multiple attack vectors (e.g., cyber, physical, and deception) to generate opportunities to achieve its objectives. These usually consist of establishing and extending its presence within the IT infrastructures of organizations to continuously exfiltrate information and undermine or hinder critical aspects of a mission, program, or organization or be in a position to do so in the future.’
Double extortion ransomware uses the same strategy so that hackers can enter and exploit the victim’s data repeatedly.
This type of ransomware is more difficult to remove.
Indeed, a double extortion attack consists of partly manual (user-dependent) and partially automated operations.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
Stages of ransomware extortion
The following are the stages of ransomware extortion:
- Ransomware is introduced into the system via a security vulnerability, a phishing email, or a drive-by download;
- Once the malware is installed on the system, it scans and maps all files and folders;
- It encrypts these files using an advanced encryption algorithm and adds the .encrypted extension to each file;
- All files are exported, and the hacker copies them;
- The ransomware sends a notice to the victim informing them that the files have been encrypted and that they must pay a ransom in exchange for the key decryption;
- If victims do not pay, hackers threaten to publish the data online.
However, the ransom payment does not guarantee data recovery.
If you are a victim of a ransomware attack, contact a company specializing in malware removal and data recovery, like HelpRansomware, immediately.
Single extortion
A single extortion ransomware attack encrypts the user’s data.
Traditional ransomware attacks assume that victims will regain access to their data and systems once they pay the ransom.
These data breaches target critical information needed for daily tasks and other digital services that can disrupt the functionality of servers or networks.
According to the report published by Veeam, 80% of attackers seek to exploit traditional systems vulnerabilities.

These include standard operating systems, hypervisors, NAS platforms, and database servers.
What is double extortion ransomware?
Double extortion ransomware is part of the more complex Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) world.
This type of ransomware involves intrusion techniques ranging from automated to manual, requiring the action of the future victim, as in the case of doxing.
The exponential increase represents a severe risk to companies, which are put at risk in terms of profits and data theft.
As SonicWall trends show, 2021 saw a +105% jump in ransomware attacks.

Altogether, a total of 623.3 million attacks.
The instability in Europe caused by the Russian conflict also suggests exponential growth in 2022.
Triple extortion ransomware
Triple extortion ransomware is an evolution from double extortion ransomware.
This threat resumes traditional attack techniques, in which the hacker demands a ransom from the company in exchange for decrypt ransomware files with a decryption key.
It is compounded by the threat of disseminating sensitive data and information.
Furthermore, triple extortion threatens to launch a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
Attackers pressure the victims and further persuade them to pay the ransom.
The most striking example of triple extortion ransomware was against Vastaamo, the largest network of private mental health providers in Finland.
As reported by the Helsinki Times, the attack shook the nation: 25,000 patients said they had received extortion attempts.
Quadruple extortion
Ransomware attacks can lead to up to four extortions.
In these cases, the attack consists of four extortion techniques:
- Encryption of all files on the device: hackers demand a ransom in exchange for the decryption key to open encrypted files;
- Threat for data dissemination on the web if the ransom is not paid;
- DoS or DDoS attacks to block the victim’s websites;
- Contact with customers, service providers, or media: hackers contact the press or the company’s customers directly, threatening to publish their data.
Cybercriminals are increasingly using these four tactics as they are highly profitable.
According to Acronis, ransomware is projected to cause $30 billion in damage by 2023.

What is the difference between ransomware and extortion?
Extortion can be considered as an evolution of ransomware.
While ransomware is born as malware to encrypt a device’s files and demand a ransom, extortion adds the threat of releasing data online.
Hackers who use ransomware double, triple, or quadruple extortion leverage different levels of threat.
Therefore, it is more complicated to remove the ransomware and decrypt files without the help of specialists.
Ransomware and extortion methods aim to access the victim’s computer or device to exfiltrate and lock all files.
While ransomware attacks many personal PCs, extortion attacks primarily target corporate networks.
The reason is simple: the amount of data, and thus profit, is rising.
In addition, while the ransomware automatically encrypts all files on the device, the extortion attack selectively encrypts the resources.
Double extortion ransomware attacks also include more advanced techniques to counter file recovery.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
Double Extortion Ransomware Attacks
Double extortion ransomware attacks attempt to extort money from the victim twice.
They usually start by encrypting the victim’s data and asking for a ransom for the decryption key.
If the victim pays, they will often be unable to decrypt their data because there is no key.
If not, the hacker will send another message with a new ransom request and a time limit for payment.
Double extortion ransomware is one of relatively new types of ransomware.
This attack is also very successful because it acts relatively calmly, and victims overlook the data breach until the ransom request.
The evolution of double extortion ransomware
The last twelve months have seen a dramatic rise in double extortion ransomware attacks.
The main reason is that companies have had to cope with a system weakening due to teleworking.
According to the UK Government, 39% of businesses report having cyber security or data breaches.

In addition, 21% of companies acknowledge that it was a more sophisticated attack, such as DoS.
The evolution of ransomware attacks continues to move toward significant gains for hackers.
Criminals have found another way to extort money, and organizations must adopt appropriate measures to overcome this new threat.
With this tactic, more is needed to back up the data for their recovery.
Ransomware types
Ransomware is constantly evolving, which is why it is a constant threat.
Consider that only some have ransomware decryption tools that you can use to recover encrypted files.
Below are the most common and profitable ransomware families for cybercriminals.
REvil
REvil is also known as Sodinokibi ransomware, a malware that encrypts files on the victim’s computer and demands a ransom for the decryption key.
The ransom request includes instructions on paying the ransom and links to Tor sites where victims can buy Bitcoin. According to IBM’s report, Revil ransomware was responsible for 37% of ransomware attacks in 2021.

REvil ransomware is impressive because it encrypts files on the victim’s computer instead of simply locking them with a password.
In addition, it uses automated systems that do not require user interaction to enter the victim’s device.
Ransomware often targets Microsoft Windows systems but encrypts files on Apple OSX and Linux machines.
It uses AES-256 encryption by default, but the victim can use RSA or Diffie-Hellman key exchange instead.

Expert Ransomware Removal
Our certified professionals have over 25 years of experience in ransomware removal, data recovery, and computer security.
WannaCry
WannaCry is malware that blocks data stored on a computer and requests a ransom to decrypt ransomware files.
It was one of the biggest attacks in history, launched in May 2017.
WannaCry ransomware is not a virus because it does not replicate, but it is a cyberworm as it spreads by infecting computers on the network.
CryptoLocker
Cryptolocker also encrypts the user’s files and then requires payment to decrypt them.
Cryptolocker ransomware was first discovered in September 2013.
The malware creators have developed several versions of the software released to the public.
They typically demand Bitcoin payments that are difficult to trace since they do not require identification or verification for transactions.
Petya
Petya malware was first detected in 2016 and is believed to be a variant of WannaCry ransomware.
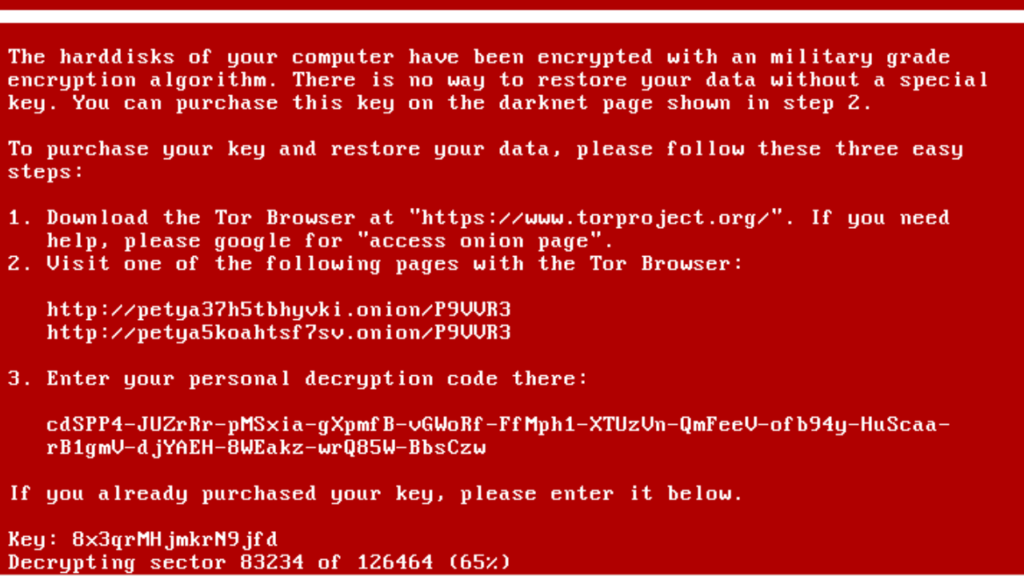
The vulnerability was discovered by British researcher Marcus Hutchins, who was credited with stopping the WannaCry exploit propagation.
Ransomware spreads through a worm that scans large networks connected to the Internet and hits vulnerable machines.
Once found, it exploits vulnerabilities in Windows and SMB Server for which Microsoft released patches earlier this year.
Ryuk
Ryuk ransomware encrypts data using the AES-256 algorithm with a key generated by a random number generator (RNG).
It also deletes shadow copies from the computer, so even if someone has an old backup of their files, they won’t be able to recover them unless they pay.
Ryuk targets specific file types like .docx, .pdf, .xlsx, .pptx, etc., making data recovery harder if the ransom is not paid.
It was first detected in August 2018 and has already been responsible for attacks on public institutions, universities, and government agencies.
Locky
Locky has been around since 2016 and is still used to extort money from people worldwide.
It affects all users with an Internet connection, so there are no limits to this ransomware.
According to Smart Data Collective, this ransomware first infected 90,000 devices per day.

Locky typically propagates via email attachments or links on social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
Ransomware Double Extortion Accounts
Conti is a ransomware discovered for the first time in November 2017.
Most likely, it was developed by a group of Russian-speaking hackers.
The malware encrypts the data on the victim’s hard drive and demands a ransom to decrypt it.
In some cases, Ransomware Accounts block files and delete them without asking for payment.
This ransomware was responsible for the attack on the government of Costa Rica.
Major double extortion ransomware families
The turning point of double extortion ransomware attacks took place in 2019 by the Maze group.
This ransomware can run on any Windows operating system and encrypts all file types, including images, videos, and documents.
Maze uses AES encryption to block the user’s files and requires payment in Bitcoin; it subsequently threatens to release the data online.
Families of double extortion ransomware have increased since Maze’s example.
Here are some:
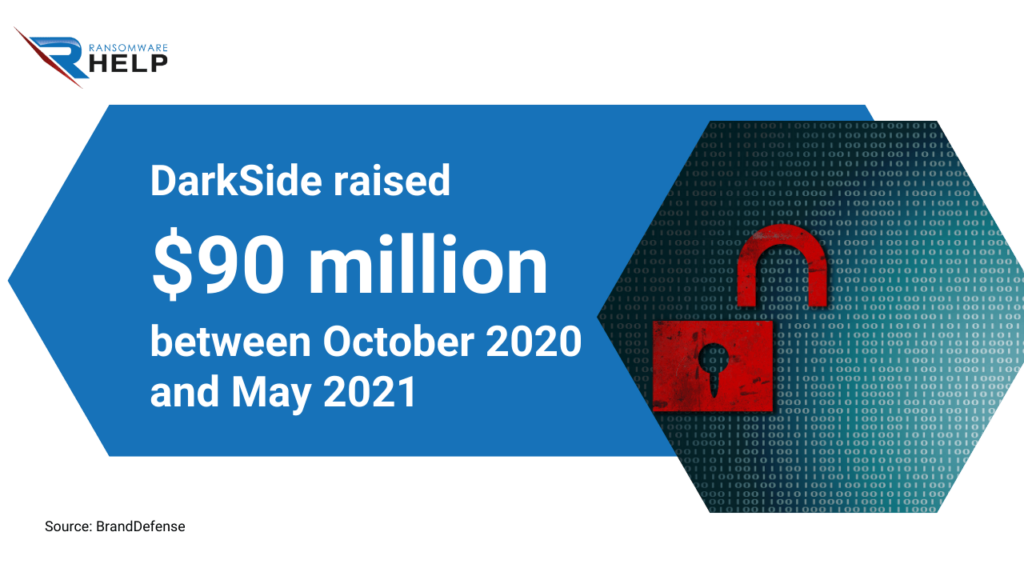
- DarkSide: as reported in the BrandDefense analysis, this ransomware raised $90 million between October 2020 and May 2021;
- Egregor: more than 150 attacks have been attributed to this ransomware;
- DoppelPaymer of the BitPaymer family: it is responsible for the attack on the Mexican state oil company Pemex which, as reported by Reuters, cost the company $5 million;
These are just some of the most common families, but evolution is constant.
Recent high-profile examples
One of the most striking cases of double extortion ransomware attack dates back to May 2021.
As stated in the press release of the US Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response:
‘On May 7, 2021, the Colonial Pipeline Company proactively shut down its pipeline system in response to a ransomware attack.’
The attack affected the largest supplier of oil products and fuel for aircraft on the US east coast.
The hackers were from the DarkSide group and stole 100GB, asking for a ransom of about $5 million in Bitcoin to restore encrypted files.
As reported in the Reuters article, Colonial Pipeline CEO Joseph Blount stated that hackers entered the company’s system using a VPN that only had single-factor authentication.
One of the companies hit by ransomware is JBS SA, the largest meat processing company in the world.
BBC reported that the Brazilian company paid a ransom of $11 million to recover the data stolen during a Conti ransomware attack.
The company claimed to have paid the ransom to protect customers who received threats.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
Why does double extortion occur?
Double extortion is an evolution of ransomware.
This tactic allows cybercriminals to earn twice as much from each cyberattack, making it harder to recover encrypted files.
The preferred targets of double extortion ransomware are large companies or organizations which handle sensitive information, such as healthcare and legal services.
It occurs for many reasons:
- The victim pays the first ransom and does not report the attack;
- After paying the first ransom, the victim contacts the police but the file recovery process is long and arduous;
- The threats continue, and the victim gives in to the ransom payment because, as in the case of hospitals, he needs access to information.
This attitude makes the victim a vulnerable target.
The best thing to do if you are a victim of a double extortion ransomware attack is to turn to a specialized company like HelpRansomware.
HelpRansomware offers various services, including ransomware deletion, file decryption, and system recovery.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What are the risks of double extortion ransomware?
The first risk of double extortion ransomware is blocking access to your data and files.
It is challenging, especially for companies that use the Internet and handle sensitive data from customers or suppliers.
Indeed, they could suffer a workflow interruption and record significant losses.
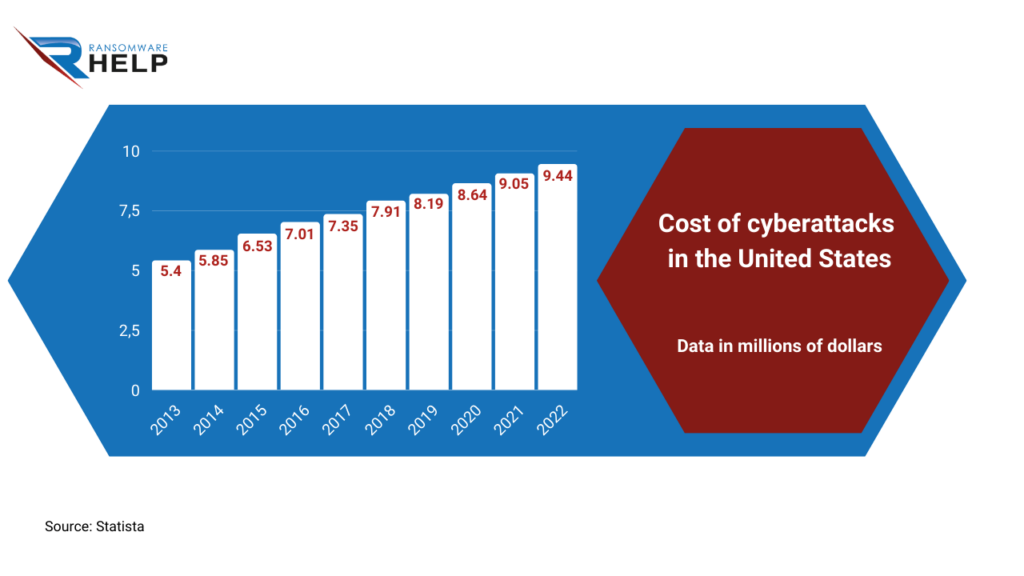
According to Statista, the cost of cyberattacks in the United States was $8.64 million in 2020 and $9.44 million in 2022.
The second risk after a ransomware attack is that hackers will not return the decrypted files; instead, they will disclose them on the web.
And paying the ransom will not prevent this.
If you pay the ransom, you expose yourself as a potential victim to future attacks.
Disseminating your organization’s or customers’, or suppliers’ sensitive data online can cause significant problems.
Apart from the loss of credibility and the damage caused to the online image, the cost for your company will also be very high for managing customer relations.
How to avoid double extortion ransomware?
To avoid being the victim of a double extortion ransomware attack, you can follow these tips:
- Make sure that anti-ransomware software is installed and updated on your computer;
- Do not visit unprotected websites;
- Perform regular antivirus scans;
- Backup data to an external hard drive or cloud storage;
- Keep your operating system up to date.
In addition, it is essential to pay close attention to emails because phishing remains one of the most common ways to infect a device.
Protect yourself from double extortion attacks
More than having a data backup is enough to protect against double extortion ransomware.
A backup protects you in case of single extortion but not from the risk of having your data disseminated on the web.
Undoubtedly, the best thing is to have your antivirus software and keep your operating system up to date.
As Microsoft has explained, businesses should always use a Zero Trust approach that mitigates risk.
In addition, companies must include several lines of defense that block illegitimate encryption, such as multi-factor authentication.
Conclusions
In this article, we have provided you with all the information you need regarding double extortion ransomware, how to avoid it, and protect your data.
From this text, you can draw the following conclusions:
- Double extortion ransomware consists of asking the victim to pay the ransom twice;
- This type of attack is dangerous since hackers can spread the data stolen from your device over the network even after the ransom is paid;
- In 2022, the average ransom paid increased nearly fivefold to $812,360 compared to the previous year;
- Double extortion ransomware increased by +500% in 2021;
- Double extortion ransomware is a part of the more complex Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) world;
- Triple extortion threatens to launch a DDoS attack; while hackers using quadruple extortion contact customers or service providers to extend the threat;
- Ransomware is projected to cause $30 billion in damage by 2023;
- The first double extortion ransomware attack perpetratedby the Maze group dates back to 2013.
Double extortion ransomware requires the help and support of a specialist team, such as HelpRansomware.
HelpRansomware can help you block ransomware and restore your data.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.



