Read the following guide and find out what CryptoLocker is, how it works and what you can do to get rid of it.
Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What is CryptoLocker?
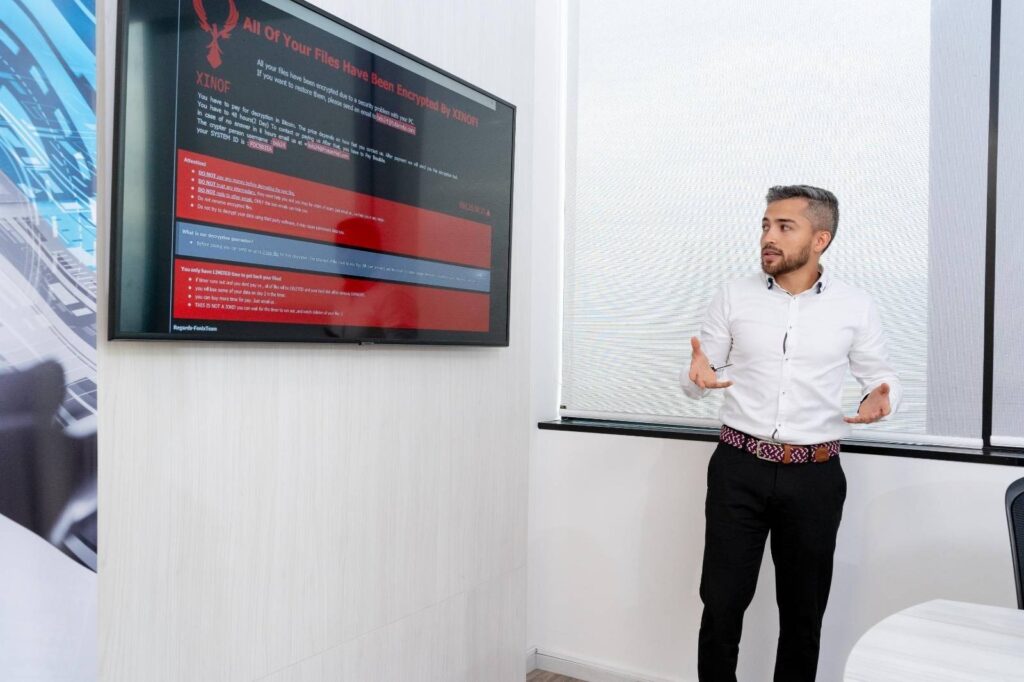
CryptoLocker is a well-known malware that is particularly harmful to any organization that works with data.
Once you execute the code, it encrypts files on shared desktops and networks and holds them hostage, requiring anyone who tries to open the files to pay a ransom to decrypt them.
For this reason, CryptoLocker and its variants have become known as ransomware.
Malware such as CryptoLocker can enter a secure network through many vectors, including email, file sharing and download sites.
The new variants have eluded antivirus and firewall technologies, and it is reasonable to expect that will soon emerge others that can circumvent preventative measures.
Nonetheless, we highly recommend you reinforce access controls to limit the extent of damage caused by an infected host.
Similarly, you can create the next line of defense by careful and repeated investigative and corrective checks.
To the fateful question: “Should you pay the ransom?” replied Cyber Reputation and Security expert Andrea Baggio: I anticipate that the answer is by no means obvious.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
What does CryptoLocker do?
Upon execution, CryptoLocker begins scanning the mapped network drives to which the host is connected to track down folders and documents.
Later it renames and encrypts the contents it has permission to modify depending on the credentials granted by the user executing the code.
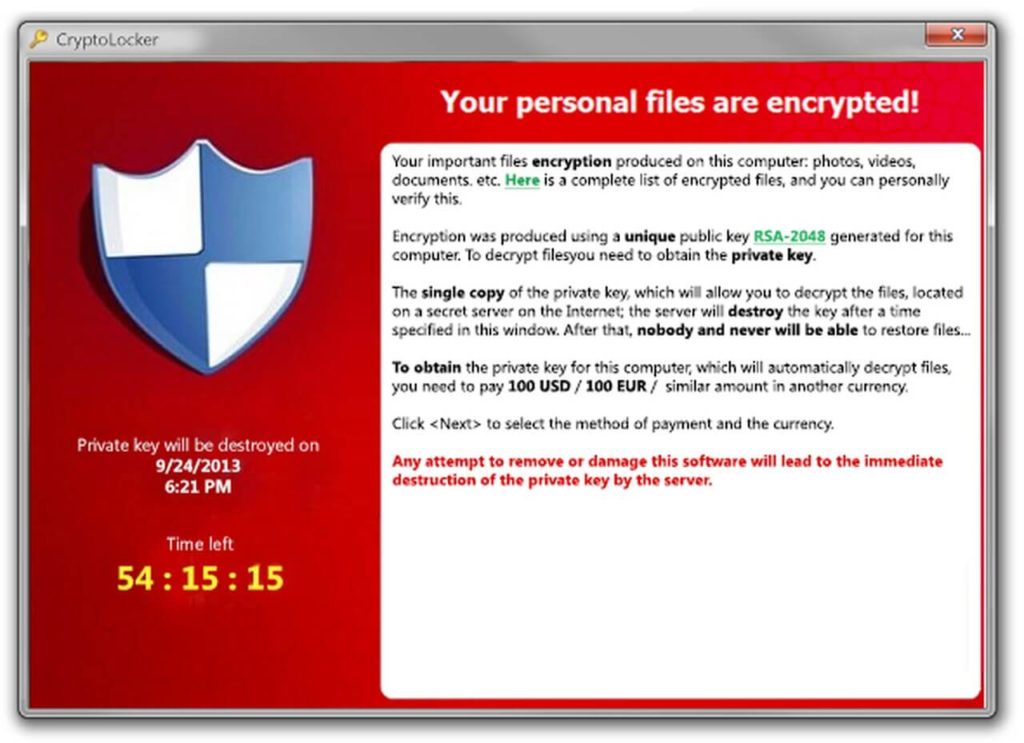
CryptoLocker uses a 2048-bit RSA key to encrypt files and renames the files by adding an extension, such as .encrypted or .cryptolocker or .[7 random characters], depending on the variant.
Finally, the malware creates a file in each affected directory by linking it to a web page that contains decryption instructions that require the user to make a payment (often via bitcoin).
Instruction file names are typically DECRYPT_INSTRUCTION.txto DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.html.
As experts discover new variants, the list of ransomware types endlessly updates.
For example, a variant known as CTB-Locker creates a single file in the directory where it first begins encrypting files, named !Decrypt-All-Files-[7 character RANDOM].TXT or !Decrypt-All-Files-[7 characters RANDOM].BMP.
How to prevent CryptoLocker?
The damage that malware can inflict is in proportion to the number of files it has access to.
Restricting access is a prudent measure that can make you reduce the amount of material that can be encrypted.
Besides offering a line of defense for malware, it will mitigate the potential exposure to other attacks by internal and external actors.
While reaching a least-privileged model is not a quick fix, you can quickly reduce exposure by removing unnecessary global access groups from ACLs.
Groups like “Everyone”, “Authenticated Users” and “Domain Users”, when used on data containers (such as SharePoint folders and sites), can expose entire user hierarchies of a company.
In addition to being easy targets for theft or misuse, these exposed datasets are highly likely to be damaged by a malware attack.
In fact, on file servers, these folders are known as “open shares” in the event that both the file system and share permissions are accessible via a global access group.
You can use dedicated technologies to find and delete global access groups.

Fast & Guaranteed Recovery
HelpRansomware provides a 100% guaranteed ransomware removal and data recovery service, with 24/7 worldwide assistance.
However, you can also locate open shares by creating a user who does not belong to any group and using that account’s credentials to examine the file-sharing environment.
You can use even the basic net commands of a Windows cmd shell to enumerate and test shares for accessibility:
- net view (enumerate nearby hosts);
- In addition net view \\ host (enumerate shares);
- net use X: \\ host \ share (map a sharing guide);
- dir / s (lists all user-readable files under the share).
You can easily combine these commands into a batch script to identify widely accessible files and folders.
Sadly, fixing these without automation can turn into a lengthy and risky process, as it’s easy to influence regular business operations if you’re not careful.
How to detect CryptoLocker
Suppose file access activity is monitored on the affected file servers.
In that case, you will observe anomalous behaviors that generate a considerable number of attempts to open, modify and create at a very rapid rate and are, therefore, easy to detect with the automation that provides valuable investigative control.
For example, if a single user account modifies 100 files in one minute, you can bet it’s an automated process.
Configure your monitoring solution to trigger an alert if you observe this behavior.
Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.
If you don’t have an automated solution to monitor file access activity, you may need to turn on native auditing.
In general, however, both native auditing and tax monitoring systems and output are unfortunately challenging to crack.
Instead of enabling and collecting native audit logs on each system, prioritize susceptible areas and consider setting up a file-sharing honeypot.
A honeypot file share is an accessible file share that contains files that look normal or valuable but are fake.
If manual commands are blocked, you will need to enable native auditing to log access and create a script to notify you when logged in the security event log (for example, using dumpel.exe).
For example, the response to a user who generates more than 100 change actions in one minute might include:
- Notification to IT and security administrators (include the username and affected computer);
- Checking the machine registry for known keys/values created by CryptoLocker;
- Get-Item HKCU: \ Software \ CryptoLocker \ Files) .GetValueNames ();
- If the value exists, it automatically disables the user.
Suppose logged access activity is safeguarded and is properly searchable.
Depending on the CryptoLocker variant, the encryption can be reversible with a real-time disassembler.
Ransomware Safety Tips
In conclusion, here are some small and simple tips to enhance your device’s security against ransomware.

- Update your antivirus and endpoint protection software – These solutions can help detect certain types of ransomware and prevent them from encrypting your files;
- Avoid Phishing Scams – Phishing emails are the most common way ransomware spreads;
- Keep backups of your documents: It is faster and easier to recover your documents from a backup than to decrypt them in case a ransomware attack has compromised them;
- Commit to following a zero-trust or least-privilege model – ransomware can only affect folders a user can write to.
- A least-privilege model restricts access to only what is absolutely necessary;
- Monitor file activity and user behavior to detect, alert and respond to potential ransomware activity.
New variants of ransomware constantly pop up: contact HelpRansomware’s dedicated security forensics team and update any ransomware signatures detected on the net.

Immediate Ransomware Help
Don’t let ransomware hold your business hostage. Our experts are ready to recover your data and secure your systems.




